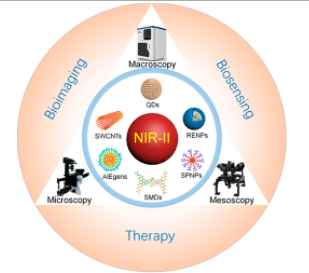
Fluorescence imaging technology has broad application prospects in basic biomedical research and clinical diagnostic testing. Near-infrared zone II fluorescence (1000-1700nm, NIR-II) imaging technology overcomes the strong tissue absorption, scattering, and autofluorescence interference faced by traditional fluorescence (400-900nm), and can achieve higher tissue penetration depth in vivo imaging with time and space resolution, it is regarded as the most promising next-generation in vivo fluorescence imaging technology. Wang Qiangbin, a researcher…