In a recent study, scientists took the first overall color picture of mice of different ages, which is an important step in understanding individual behavior. The results of the study, published in the journal Science, are key to revealing the mechanisms of learning disabilities, dementia, and how memory is affected by age. Synapses are important connections between brain cells to transmit electrical and chemical information. Synapse damage is associated…
New Article
Science: Structurally Revealing the Mechanism of INSTI Drug Binding to HIV Intasomes
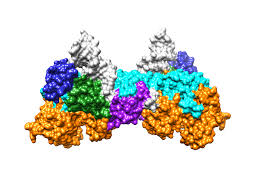
In a new study, researchers from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive Diseases, the National Cancer Institute, the Shake Institute for Biology, and the Scripps Research Institute have discovered a key part of how a powerful class of HIV drugs binds the HIV intasome. By solving for the first time the three-dimensional structure of this intasome when combined with different drugs, they discovered what makes this class of drugs…
New Study Redefined the Understanding of T Cell Recognition
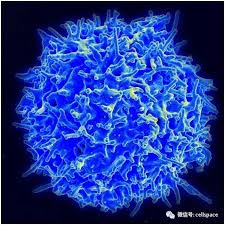
T cells are a key component of our immune system and play a key role in protecting us from harmful pathogens such as viruses and bacteria, as well as cancer. The more we know about how they recognize, act on, or even kill infected cells or cancer cells, the closer we can get to developing drugs and treatments for various diseases. In a new study, researchers from Monash University…
Using New Imaging Technology to Reveal the Mechanism of Cancer Cell Growth and Spread in Colon
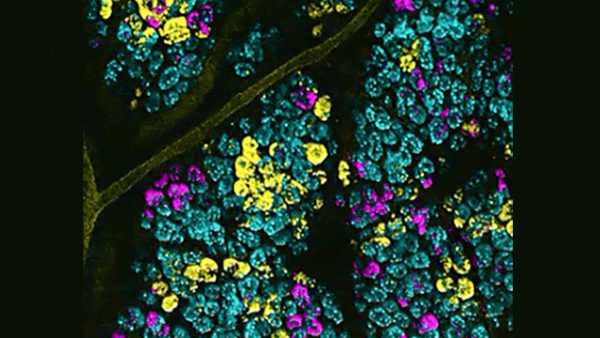
According to a recently published report in Nature Communications, scientists from Duke University Medical Center and other institutions revealed how stem cell mutations quietly occur and spread to a wide range of areas in the colon until they eventually dominate and develop into malignant tumors. By using an innovative model system in mice, researchers can visually mark colon cancer mutations by promoting stem cell luminescence, and then they can observe…
Unraveling the Mystery of the Structure of the Potassium-Chloride Cotransporter
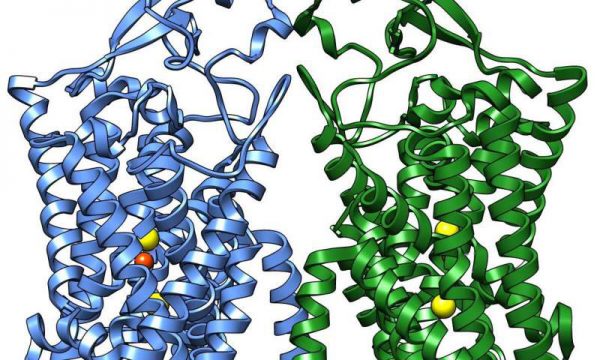
Once the homeostasis of potassium, sodium, and chloride in human cells is out of balance, it will lead to a series of diseases such as hypertension, depression, and epilepsy. At the cell membrane, there is a class of proteins known as cation-chloride cotransporters that effectively regulate ion homeostasis in the cell. The group of Guo Jiangtao of Zhejiang University School of Medicine solved the 2.9-Å high-resolution cryo-EM structure of a…
Fluorescent Probes Provide a Whole View of Drug Delivery in Cells

Selecting the most effective molecules for drug delivery usually requires trial and error. Recently, researchers at Cornell University have revealed how to transport molecules behave in living cells, providing some basis for judgment. The drug delivery system controls when and where the drug is released in the body. The principle of many drug delivery systems is to connect antibodies (looking for targets such as cancer cells) with drugs used…
Visualizing How HIV Multiplies In vivo with High Resolution
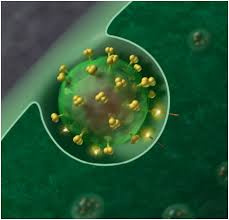
To treat a disease, we must understand how it arises. In a new study, researchers from Germany, Britain, France, Spain, and Australia now use high-resolution imaging to visualize how HIV spreads between living cells at millisecond resolution. Using ultra-high resolution STED fluorescence microscopy, they provide the first direct evidence that the HIV virus builds a lipid environment for its own replication. In response, they created a method to study how…
Scientists Filmed the First Video of T Cells Being “Educated”

Immunologists from the University of Texas at Austin first captured a video of T-cells being educated at an early stage and the results were published in the journal Nature Communications. The study showed a new imaging technology that allows video recording, which is expected to fight against autoimmune disorders disease, such as type 1 diabetes. T cells are one of the most powerful weapons against many diseases in the…
Fetal’s Head Might Be Reconstructed During Labor

The three-dimensional images captured by scientists through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology, showed how the head and skull are shaped when passing the birth canal before childbirth. Olivier Ami of the University of Kloofen, France, and his colleagues published these latest research results in PLOS ONE. Doctors have known that the baby’s head shape might be changed during labor and these changes are so-called “head molding”, which occurs in…
Many Studies Show that A Computational Method that Thermally Stabilizes G-protein-coupled Receptors is Promising in The Analysis of Receptor Structures

Researchers from the Moscow Institute of Physical Science and Technology (MIPT), the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech) and the University of Southern California (USC) have developed a new computational method to design thermally stable G Protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which are very effective in developing new drugs. This method has been shown to be useful for obtaining the structure of several major human receptors. An overview of this new…
