The stoma is a window for material and information exchange between plant and environment. Stomata mediate the adaptation of plants to the external environment by sensing and decoding various environmental signals, such as drought, CO2, and ozone. In addition, stomata are the invasion channels of pathogenic microorganisms and participate in the immune response of plant disease resistance. Stomata control CO2 uptake and water transpiration, and their opening and closing are…
cryoET
Scientists Reveal the 3D Structure of Special Complexes Responsible for Gene Expression in Cells
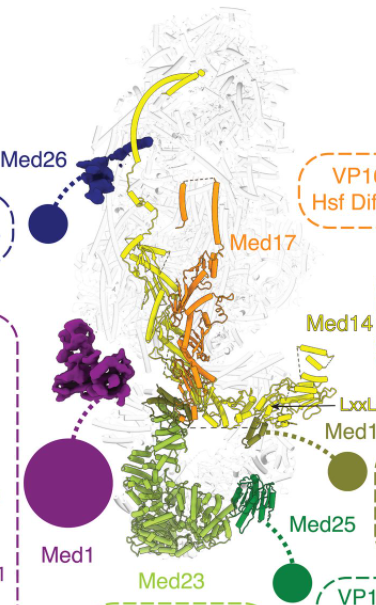
Recently, in a research report entitled “Structure of the human mediator bound transcription pre-initiation complex” published in the journal Science, scientists from Northwestern University and other institutions in the United States first observed multiple subunit machines responsible for regulating gene expression in human cells through research. According to the researchers, the complex called Med-PIC (mediator-bound pre-initiation complex) is the key determinant of which genes are activated and which genes…
Studies Reveal the Structural Basis of Serotonin Receptor as a Target of Depression
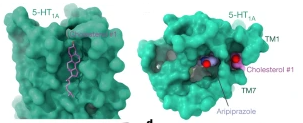
Serotonin is an important neurotransmitter, which plays a role in the brain and endows people with the ability to feel happiness. Therefore, it is also known as a “happy neurotransmitter”. The serotonin system is involved in a wide range of physiological functions of the human body, including the regulation of brain memory, cognition, emotion, learning, and addiction. The disorder of the serotonin system may cause a variety of mental diseases…
Mechanism of Glutamate Transporter in Cell Membrane
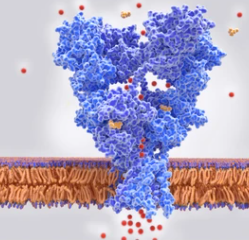
In a new study, researchers from the University of Sydney in Australia and the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign reveal the shape of one of the most important molecular machines in our cells, the glutamate transporter, which helps to explain how our brain cells communicate with each other. The related research results were published online in Nature with the title of “Glutamate transporters have a chloride channel with two…
Study Revealed the Molecular Mechanism of A Special Heme Copper Terminal Oxidase Using Two Electron Donors

Sun Fei research group of Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Hartmut Michel research group of Max Planck Research Institute, Germany published a research paper entitled “The unusual homodimer of a heme copper terminal oxide allow itself to utilize two electron donors” in German Applied Chemistry. In this work, a special heme copper terminal oxidase from thermophilic bacteria was studied. By analyzing its high-resolution freeze electron microscope…
Study Revealed the Structural Basis of Assembly Factor Psb27 Regulating the Assembly and Repair of Photosystem II
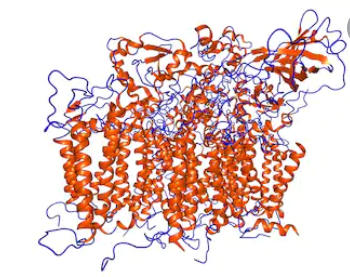
Photosynthesis is a process of large-scale utilization of solar energy to synthesize carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds and release oxygen. Photosystem Ⅱ (PSⅡ) is located on the thylakoid membrane of oxygen releasing photosynthetic organisms, which is an important place for the oxidation of photosynthetic water. PSⅡ core complex has the function of photosynthesis and oxygen releasing, which is a pigment membrane protein and composed of 20 protein subunits,…
The High-resolution Structure of de novo DNA Methyltransferase and Natural Substrate Nucleosomes
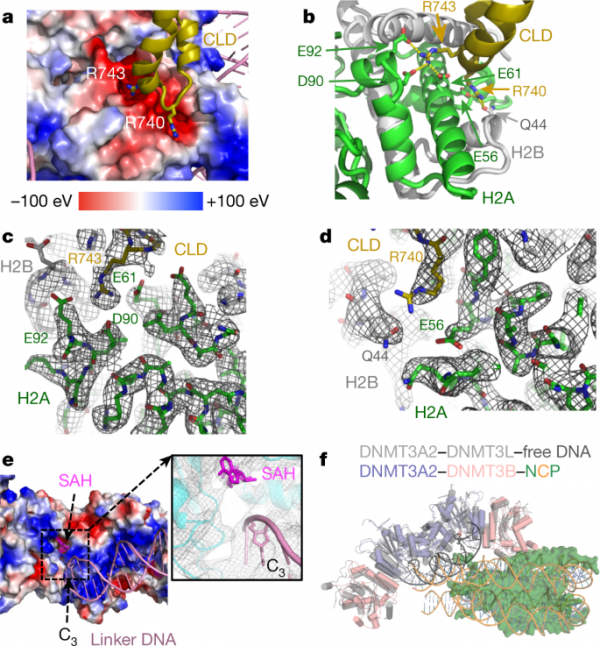
Recently, the Xu Huaqiang group of the Shanghai Pharmaceutical Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in cooperation with the Peter Jones group and Karsten Melcher group of the US Van Andel Research Institute, used cryo-electron microscopy to analyze the high-resolution structure of the de novo DNA methyltransferase (DNMT3A2/DNMT3B3) and the natural substrate nucleosome. Research describes the binding mode of DNMT3A2/DNMT3B3 and the nucleosome, and proposes a model of genome-wide DNA…
Nature: A Human Antibody Can Potently Neutralize Multiple Coronaviruses Including Sars-Cov and Sars-Cov-2
In a new study, researchers from the Swiss Humbs Biomed SA and the University of Washington found an antibody identified for the first time in blood samples from a patient with the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS, commonly known as atypical pneumonia) in 2003 which can inhibit related coronaviruses, including the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 that causes 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19). This antibody, called S309, is currently in rapid development and…
Structural Basis of Poxvirus Transcription Revealed
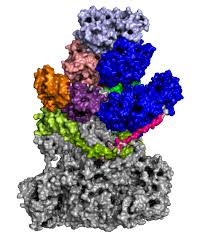
In order for viruses to proliferate, they usually need to be supported by infected cells. In many cases, the molecules they need to replicate their own genetic material are only found in the nucleus of the host cell before infecting other cells in the vicinity. But not all viruses enter the nucleus. Some viruses stay in the cytoplasm and must, therefore, be able to replicate their genetic material independently. To…
Unraveling the Mystery of the Structure of the Potassium-Chloride Cotransporter
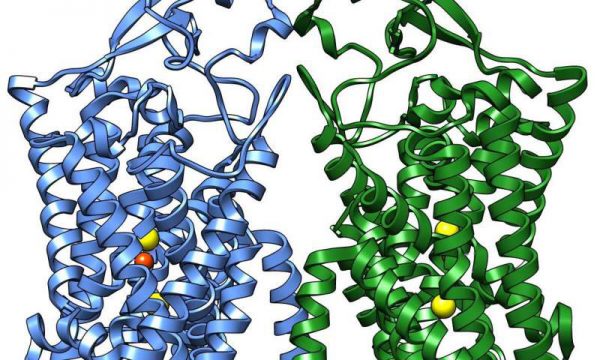
Once the homeostasis of potassium, sodium, and chloride in human cells is out of balance, it will lead to a series of diseases such as hypertension, depression, and epilepsy. At the cell membrane, there is a class of proteins known as cation-chloride cotransporters that effectively regulate ion homeostasis in the cell. The group of Guo Jiangtao of Zhejiang University School of Medicine solved the 2.9-Å high-resolution cryo-EM structure of a…
